Kubectl 常用命令备忘
1、Kubectl 自动补全
BASH
1
2source <(kubectl completion bash) # 在 bash 中设置当前 shell 的自动补全,要先安装 bash-completion 包。
echo "source <(kubectl completion bash)" >> ~/.bashrc # 在您的 bash shell 中永久的添加自动补全您还可以为 kubectl 使用一个速记别名,该别名也可以与 completion 一起使用:
1
2alias k=kubectl
complete -F __start_kubectl kZSH
1
2source <(kubectl completion zsh) # 在 zsh 中设置当前 shell 的自动补全
echo "if [ $commands[kubectl] ]; then source <(kubectl completion zsh); fi" >> ~/.zshrc # 在您的 zsh shell 中永久的添加自动补全
2、Kubectl 上下文和配置
- 设置 kubectl 与哪个 Kubernetes 集群进行通信并修改配置信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25kubectl config view # 显示合并的 kubeconfig 配置。
# 同时使用多个 kubeconfig 文件并查看合并的配置
KUBECONFIG=~/.kube/config:~/.kube/kubconfig2 kubectl config view
# 获取 e2e 用户的密码
kubectl config view -o jsonpath='{.users[?(@.name == "e2e")].user.password}'
kubectl config view -o jsonpath='{.users[].name}' # 显示第一个用户
kubectl config view -o jsonpath='{.users[*].name}' # 获取用户列表
kubectl config get-contexts # 显示上下文列表
kubectl config current-context # 展示当前所处的上下文
kubectl config use-context my-cluster-name # 设置默认的上下文为 my-cluster-name
# 添加新的集群配置到 kubeconf 中,使用 basic auth 进行身份认证
kubectl config set-credentials kubeuser/foo.kubernetes.com --username=kubeuser --password=kubepassword
# 在指定上下文中持久性地保存名字空间,供所有后续 kubectl 命令使用
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace=ggckad-s2
# 使用特定的用户名和名字空间设置上下文
kubectl config set-context gce --user=cluster-admin --namespace=foo \
&& kubectl config use-context gce
kubectl config unset users.foo # 删除用户 foo
3、Apply
apply 通过定义 Kubernetes 资源的文件来管理应用。它通过运行 kubectl apply 在集群中创建和更新资源。 这是在生产中管理 Kubernetes 应用的推荐方法。 参见Kubectl 文档。
4、创建对象
- Kubernetes 配置可以用 YAML 或 JSON 定义。可以使用的文件扩展名有 .yaml、.yml 和 .json。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45kubectl apply -f ./my-manifest.yaml # 创建资源
kubectl apply -f ./my1.yaml -f ./my2.yaml # 使用多个文件创建
kubectl apply -f ./dir # 基于目录下的所有清单文件创建资源
kubectl apply -f https://git.io/vPieo # 从 URL 中创建资源
kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx # 启动单实例 nginx
kubectl explain pods,svc # 获取 pod 清单的文档说明
# 从标准输入创建多个 YAML 对象
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: busybox-sleep
spec:
containers:
- name: busybox
image: busybox
args:
- sleep
- "1000000"
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: busybox-sleep-less
spec:
containers:
- name: busybox
image: busybox
args:
- sleep
- "1000"
EOF
# 创建有多个 key 的 Secret
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: mysecret
type: Opaque
data:
password: $(echo -n "s33msi4" | base64 -w0)
username: $(echo -n "jane" | base64 -w0)
EOF
5、查看和查找资源
1 | # get 命令的基本输出 |
6、更新资源
1 | kubectl set image deployment/frontend www=image:v2 # 滚动更新 "frontend" Deployment 的 "www" 容器镜像 |
7、部分更新资源
1 | # 部分更新某节点 |
8、编辑资源
- 使用你偏爱的编辑器编辑 API 资源。
1
2kubectl edit svc/docker-registry # 编辑名为 docker-registry 的服务
KUBE_EDITOR="nano" kubectl edit svc/docker-registry # 使用其他编辑器
9、对资源进行伸缩
1 | kubectl scale --replicas=3 rs/foo # 将名为 'foo' 的副本集伸缩到 3 副本 |
10、删除资源
1 | kubectl delete -f ./pod.json # 删除在 pod.json 中指定的类型和名称的 Pod |
11、与运行中的 Pods 进行交互
1 | kubectl logs my-pod # 获取 pod 日志(标准输出) |
12、与节点和集群进行交互
1 | kubectl cordon my-node # 标记 my-node 节点为不可调度 |
12.1、资源类型
- 用于探索 API 资源的其他操作
1
2
3
4
5
6kubectl api-resources --namespaced=true # 所有命名空间作用域的资源
kubectl api-resources --namespaced=false # 所有非命名空间作用域的资源
kubectl api-resources -o name # 用简单格式列举所有资源(仅显示资源名称)
kubectl api-resources -o wide # 用扩展格式列举所有资源(又称 "wide" 格式)
kubectl api-resources --verbs=list,get # 支持 "list" 和 "get" 请求动词的所有资源
kubectl api-resources --api-group=extensions # "extensions" API 组中的所有资源
12.2、格式化输出
要以特定格式将详细信息输出到终端窗口,可以将
-o或--output参数添加到支持的kubectl命令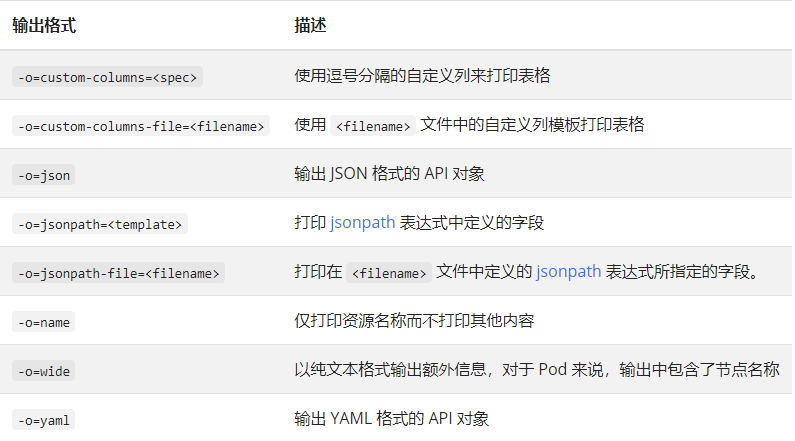
使用 -o=custom-columns 的示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6# 集群中运行着的所有镜像
kubectl get pods -A -o=custom-columns='DATA:spec.containers[*].image'
# 除 "k8s.gcr.io/coredns:1.6.2" 之外的所有镜像
kubectl get pods -A -o=custom-columns='DATA:spec.containers[?(@.image!="k8s.gcr.io/coredns:1.6.2")].image'
# 输出 metadata 下面的所有字段,无论 Pod 名字为何
kubectl get pods -A -o=custom-columns='DATA:metadata.*'
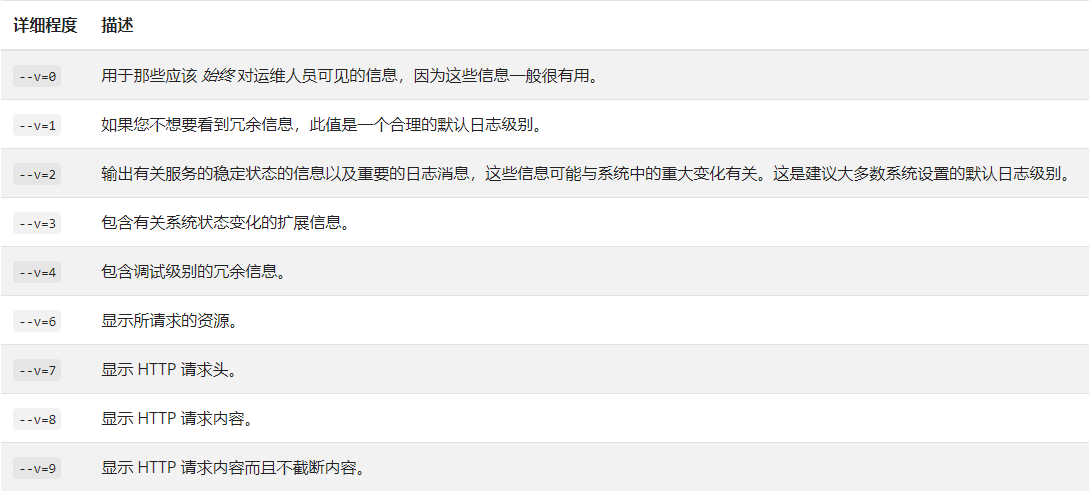
12.3、Kubectl 日志输出详细程度和调试
- Kubectl 日志输出详细程度是通过 -v 或者 –v 来控制的,参数后跟一个数字表示日志的级别。 Kubernetes 通用的日志习惯和相关的日志级别在 这里 有相应的描述。